Eunike Velleuer, Carsten Carlberg
Fanconi anaemia as a human model of accelerated epigenetic and immune ageing
Ageing Research Reviews 2026, Volume 115
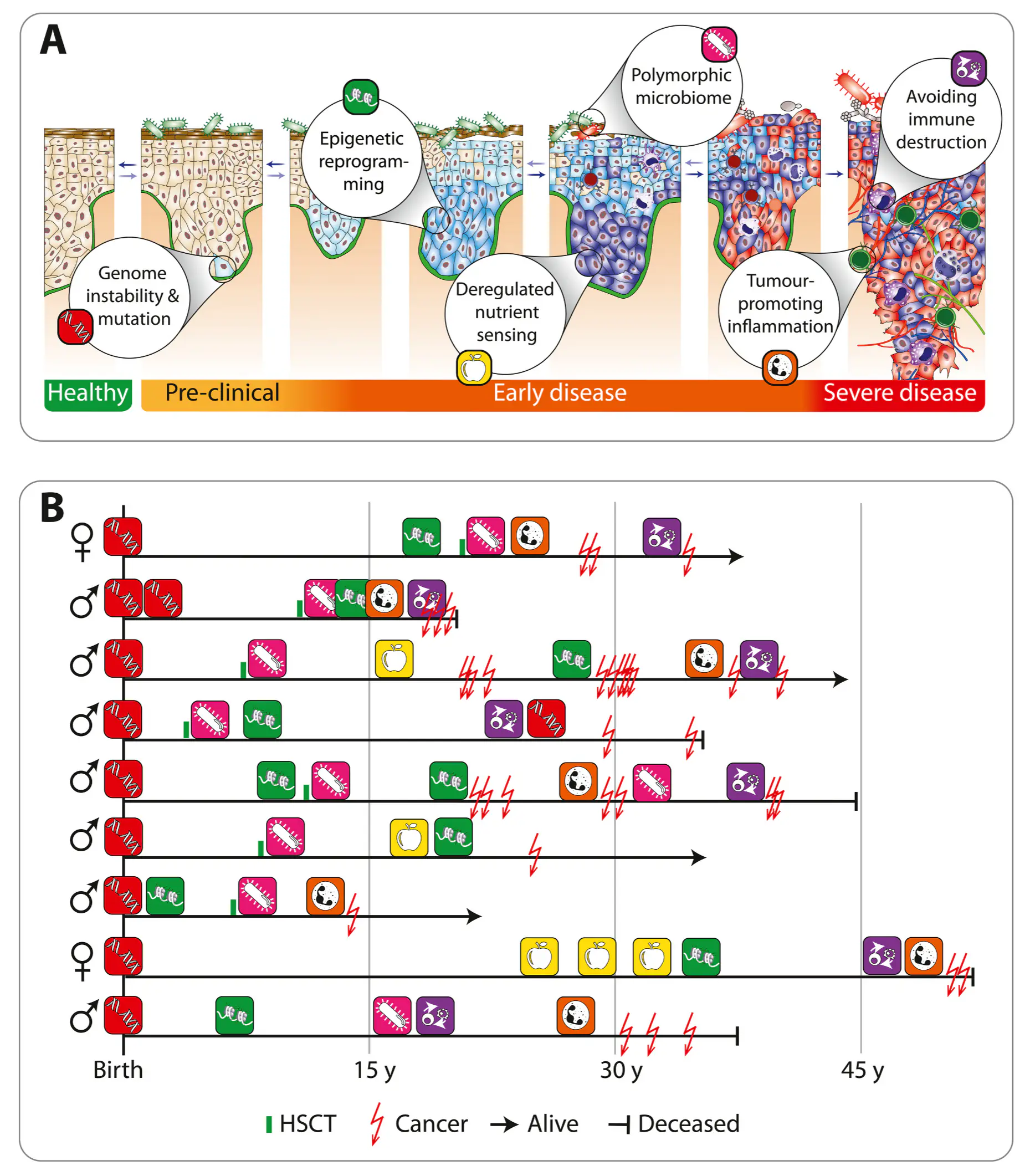
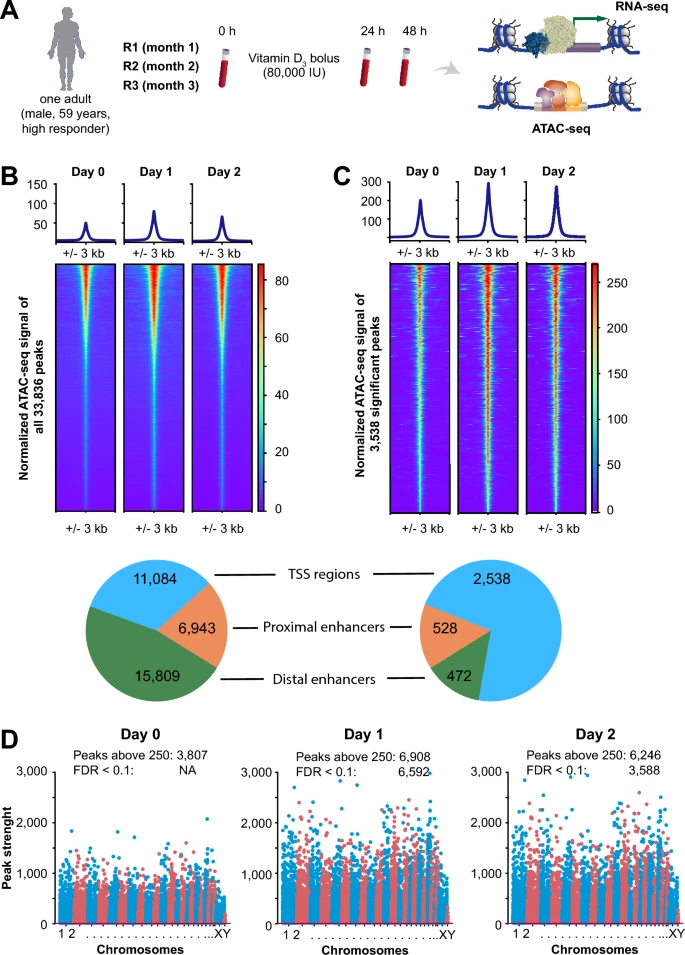
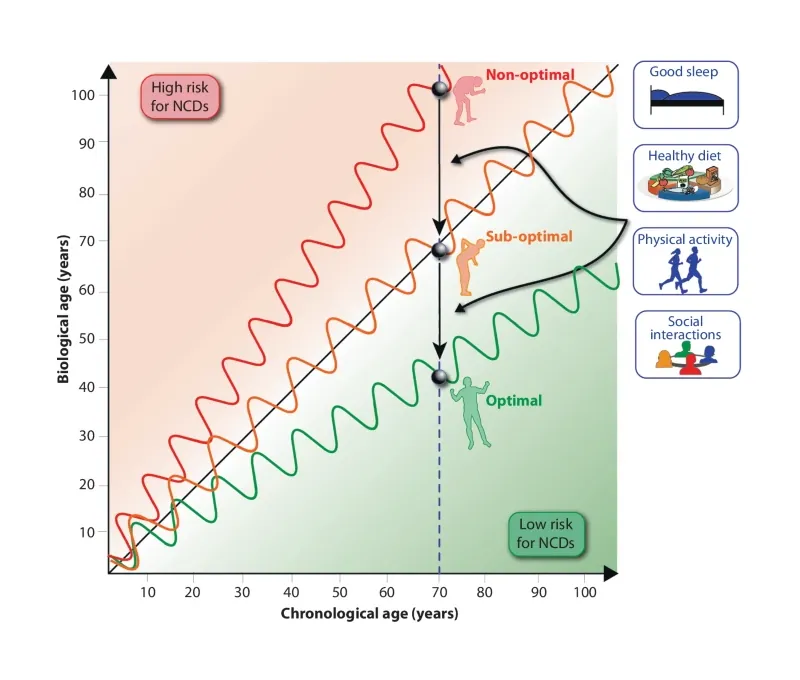
Fanconi anaemia (FA) is a DNA-repair disorder that compresses multiple hallmarks of ageing into childhood and early adulthood. Persistent genomic instability in FA precipitates oxidative stress, inflammatory remodelling, and metabolic reprogramming, which together erode epigenetic integrity and immune competence. Here we provide evidence FA-specific DNA-repair failure is linked to mitochondrial metabolism, nutrient-sensing networks, and immune dysfunction. In this context, we discuss how these interactions accelerate epigenetic drift and cancer susceptibility. We propose FA as a human “time-lapse” model to separate the sequence and interdependence of selected ageing hallmarks, such as genome instability, epigenetic deregulation, stem cell exhaustion, and immunosenescence, which together contribute to a markedly increased risk of early cancer development. We further highlight nutrigenomic mechanisms, including vitamin D-dependent chromatin remodelling and redox-sensitive cofactors, that modulate epigenetic states and immune resilience. Framing FA within the broader framework of ageing biology suggests testable biomarkers and precision-prevention strategies aimed at stabilising the epigenome, delaying carcinogenesis, and prolonging healthspan.
View full text